About Centre
The salt affected soils are an important ecological entity in the landscape of any arid and semi-arid regions in India; such problematic soils occupy nearly 6.73 million ha and represent a serious threat to our ability to provide food, livelihood security of the burgeoning population.
However, in Uttar Pradesh the salt affected soils accounts for about 1.37 million ha. The majority of these soils are having pHs > 10, exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) >15 and varying electrical conductivity (EC). The soil sodicity is a serious problem of the Indo-Gangetic plain affecting the productivity and livelihood of the people. In order to combat the challenges and threat posed due vast area of salt affected soils in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, Indian Council of Agricultural research (ICAR) had decided to establish a Regional Research Station of CSSRI, Karnal at Lucknow during IX Five-year plan and it was formally established on 27 October, 1999. Since its inception, the institute has been pursuing interdisciplinary research on reclamation and management of salt affected and waterlogged soils. The centre has now grown into an internationally recognized centre of excellence in salinity research. The following were the main areas of investigation.
- Alkali land reclamation for crop production through agro-chemical methods.
- Reclamation and management of waterlogged soils
- Horticulture and Agro-forestry
- Improving sustainability of crop production through use of salt tolerant varieties.
Location and Climate
The present location of office cum laboratory building of Central Soil Salinity Research Institute, Regional Research Station, Lucknow is at old Jail Road, Near Manyawar Kanshiram Smarak Sthal, Alambagh while its experimental research site (Shivri Farm) is located at Mohan Road, Lucknow. It lies in the Central part of the Indo-Gangetic Plain with an average rainfall of 800 mm of which the majority of rainfall occurs during July-September. The groundwater table depth of the research site fluctuates seasonally between 5-7 m. Baring the months of july and August, the evaporation exceeds rainfall. The soils are classified as Typic Natrustalfs
Mandate
The RRS, Lucknow was established with the following mandate:
-
To develop appropriate hydraulic/agrochemical/biological technologies for reclamation/amelioration of relatively heavier sodic soils of central Indo-Gangetic plains, with surface drainage congestion and high water table,
-
To conduct research on use of sodic (high RSC) water and agro-industrial effluents,
-
To collaborate with regional agencies for achieving the above goals
-
To act as a centre of training in sodicity/salinity research in the region and provide consultancies.
Research
A. Reclamation and Management of sodic Soils
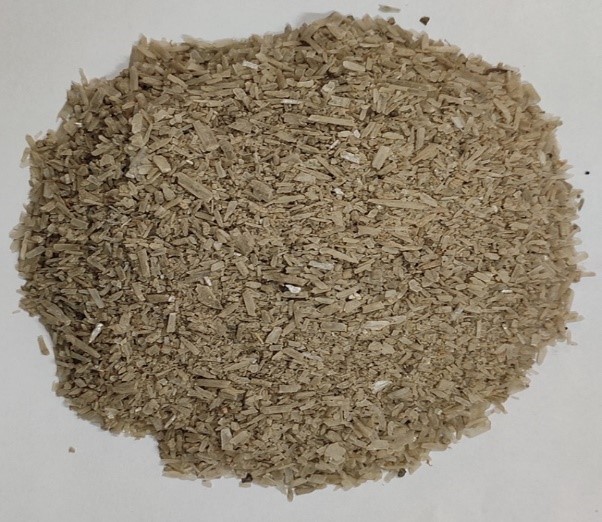
Marine Gypsum as alternate to mineral gypsum for sodic soil reclamation
- The marine gypsum, which is a waste/by-product of common salt (NaCl) manufacturing process has been found to be alternative to mineral gypsum for sodic soil reclamation.
- The reclamation of degraded sodic soils with pH 10.2 and the results showed that it could be used effectively as an alternative to mineral gypsum in the reclamation of degraded sodic soils.
- Because of higher purity (92%) of marine gypsum compared to mineral gypsum (70%), the quantity required is 23.8% lesser than the mineral gypsum in the reclamation of one hectare of sodic soils having pH above 10.
- A saving of Rs. 21,360/- per hectare for reclamation of sodic soil with respect to cost of amendment.


Use of coal combustion fly ash for reclamation of sodic soils
- The Ca is one of the dominant cations in flyash that plays a vital role in agglomeration and flocculation of the clay particles of sodic soils.
- It was identified that one-time application of flyash @ 2.5% along with 25GR mineral gypsum and/or green manuring improved productivity of degraded sodic soils in wake of declining availability of mineral gypsum.
Native CaCO3 dissolution for reclamation of calcareous sodic soils
- The native CaCO3 dissolution can be enhanced with addition of sulphonated presumed in the calcareous sodic soils of Bihar.
- Release of Ca+Mg ions from soil amended with presumed @ 10 tha-1 at field capacity moisture increased by 15.2 to 22.8 per cent.
- The study indicates that native CaCO3 dissolution can help in ameliorating sodic effect when presumed was applied to sodic calcareous soils.
Water hyacinth as organic amendment for sodic soils
- It is difficult to reclaim calcareous sodic soils having high clay content through chemical amendment. The water hyacinth having more than 80% organic matter is commonly available in village ponds.
- The release of Ca+Mg increased due to dissolution of native CaCO3 was 14.4 to 22.6 per cent higher in water hyacinth amended soils as compared to no water hyacinth application.
- The application of water hyacinth as soil amendment improved soil physico-chemical and biological properties, improved infiltration, bulk density and enhanced productivity of rice and wheat by 28 and 19 percent in calcareous sodic soils.
Composting of MSW for sustainable reclamation of sodic soils
- On-farm composting with combined use of municipal solid wastes and agricultural wastes was developed as an appropriate technology to produce cost effective nutrient rich quality compost.
- Application of on-farm MSW compost with reduced dose of gypsum in sodic soil improved the soil properties of sodic soils having ameliorative potential.
- With the introduction of this technology sodic soil reclamation cost can be reduced to 35.6% due to saving of 50% gypsum by the substitution of MSW compost @10 t ha-1.
Microbial Formulations
HALO-Azo: Halophilic N-fixer liquid microbial formulation
- The liquid microbial formulation contains halophilic strains of Azotobacter, free-living nitrogen fixer in soil and has IAA and siderophore production attributes.

- Its soil application promotes N fixation and supplements nitrogen requireme
- nt of crops to promote plant growth under salt stress.
- It is useful in all field crops viz. rice, wheat, mustard, fodder, millets and vegetable crops.
- When applied as seed inoculants, it can augment 15-20 kg N/ha to the soil. It helps in increasing crop yield by 10-15 percent.
- The liquid formulation keep soils biologically active and helps in soil health maintenance, having longer shelf life and easy to use as seed inoculation, seedling root dip and soil application.
HALO-PSB: Halophilic Phosphate solubilizer liquid microbial formulation

- Formulation contains highly efficient salt tolerant/halophilic strains of P solubilizing bacteria.
- It ensures better root development, nutrient uptake and thereby vigorous crop growth under salt stress.
- Liquid formulation of Halo-PSB is useful for rice, wheat, mustard, maize and vegetables crops.
- The liquid formulation is tested to suit soils with pH in the range of 7.5 to 9.7.
- Inoculation of P solubilizer helps to augment 15 to 20 kg P2O5 ha-1. Keep soils biologically active and helps in soil health maintenance.
- It is convenient to use as seed
- inoculation, seedling root dip and soil application.
Halo-MIX: Microbial Formulations for Salt Affected Soils

- The consortia of compatible halophilic N-fixers, P solubilizers and Zinc solubilizing bacteria, prepared in standardized media.
- These can be used either for seed treatment or soil application.
- These microbes remediate the rhizospheric environments and allow movement of water and nutrients alleviating salt stress.
- Plant available macro and micro-nutrients like N, P and Zn that are deficient in most of the soils can be mobilized through microbes and make available to plants in a gradual manner under salt stress.
- Bioformulations are also ideal input for reducing the cost of cultivation and for promoting organic farming on salt affected soils. This technology has been commercialized for mass scale production.
Halo-Zinc: Microbial Formulation for zinc solubilization in Salt Affected Soils

- Salt tolerant (halophilic) bacterial strains of Zinc solubilizing bacteria (ZSB) in suitable standardized media.
- These microbes enhance availability of deficient zinc in soil and maintains soil health
- It minimizes environmental pollution and cut down on the use chemical.
- It can be used either for seed treatment or soil application and formulation helps in reducing the cost of cultivation and for promoting organic farming on salt affected soils
Halo-CRD: Microbial Formulation for Crop Residue Decomposition
- The halophilic lignocellulolytic microbes have the potential to degrade the rice crop residues to avoid residue burning.
 These efficient degrading microbes helps in recycling nutrients and buildup of soil C facilitate reclamation of sodic and saline-sodic soils.
These efficient degrading microbes helps in recycling nutrients and buildup of soil C facilitate reclamation of sodic and saline-sodic soils.- It has been tested and validated at multi-locations and found that inoculation of residue with Halo-CRD helps in faster in-situ degradation of paddy residues to the extent for easy ploughing for next crop sowing. It is easy to apply and eco-friendly approach for management of residues for nutrient recycling and soil health management to avoid burning.
CSR-BIO – Microbial Formulation for horticultural crops in salt affected and normal soils
- Developed a potential bio-growth enhancer CSR-BIO using growth promoting microbial consortia (Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus licheniformis, and Trichoderma harzianum) in a single dynamic patented culture media.
- It enables the production of commercial vegetable crops in salt affected soils of pH 9.2.
- It helps in increasing yield upto 18-22 percent in horticultural and vegetable crops apart from protecting against soil borne diseases like blight and wilt.
ICAR-FUSICONT – A biocontrol agent for the management of the banana Panama wilt
- ICAR-FUSICONT is a bio-formulation developed using antagonistic fungal strain Trichoderma reesei CSR T3 in a unique IPR protected media with a dynamic substrate.
- It has an effective shelf life of 14-18 months when stored at ambient temperature validated at three ecosystem of the sub-continent.
- It is the only validated effective formulation in the country for the management of devastating outbreak of banana Fusarium wilt disease caused by TR-4.
CSR-Compost Enricher Block

- The compost enricher block has municipal solid waste compost infused with active beneficial halophilic micro-organisms.
- It helps is stabilizing compost and mineralize soil nutrients viz. N, P, K and Zinc.
- The microbially enriched municipal solid waste compost (MSWC) is found to be effective in ameliorating salt affected soils and enhancing crop growth and yield under salt stress.
- It is eco-friendly and cheap approach for taking additive advantages from the compost. This technology has been approved for commercialization.
GypKit: A field kit for rapid assessment of soil sodicity and estimating gypsum requirement to reclaim sodic soil

- Gypsum requirement estimation of sodic soil for chemical reclamation is essentially required to avoid any over or under use of the amendment.
- The laboratory method for determination of gypsum requirement of sodic soils is very tedious and time consuming.
- This kit is user friendly and can be useful for farmers for assessing soil sodicity and estimating quantum of gypsum required for sodic soil reclamation to optimize crop production.
- This field kit can be easily used at the farm and does not require electricity or any power source.
- It is tested and validated with traditional laboratory method. This has been commercialized for mass scale production.
SQASS: Desktop Software and Mobile Application


- A Desktop based software application and Android Mobile App as Decision Support system for Soil quality assessment and yield prediction of salt tolerant and traditional crop varieties in sodic soils.
- It is based on Relative Soil Quality and Production Efficiency indices developed for confirming the soil and weather parameter contributing towards soil quality and production efficiency of sodic soil.
- It helps in devising reclamation strategy and soil health management.
- The application has been submitted for grant of copyrights.
B. Management of Waterlogged Sodic Soil
Land modification based integrated farming system models for waterlogged sodic soils


- The major share of waterlogged sodic soil in UP is lying in Sharda Sahayak canal command. Allahabad, Raebareli, Pratapgarh, Unnao and Hardoi are the hardest hit area due to sodicity.
- Gypsum based sodic land reclamation technology is not effective under shallow water table conditions (< 2.0 m below ground surface).
- The FPBIFS model for reclamation and management of waterlogged sodic soils was developed. The model promotes crop diversification for cereals within a period of two years and vegetables thereafter.
- The RASBBIFS model was beneficial for vegetables diversification and fruit crops such as guava, banana, papaya and lemon have been successful. Soil pH and EC reduction have been achieved to the sustainable level in these models.
- The models have tremendous potential for re-storing and rejuvenating local ecosystems and environment.
C. Management of Marginal Quality Waters
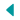
Ground Water Recharge through Pond and Recharge Shaft
- Fluoride removal from large water volume may be expensive too for animal use. Technique available for removal of fluoride from water has limitations and not adapted by the rural masses.
- Groundwater recharge for dilution of fluoride in groundwater through village pond and a recharge shaft developed as fluoride remediation technique.
- Rainwater harvested from village was collected in a adjoining pond and recharged through a recharge shaft and pond successfully.
- Fluoride concentration was successfully brought below 1.5 ppm threshold making groundwater safe for drinking purpose. The technique is application for dilutions of other pollutants too.

Rainwater Storage Structure
- A rain water storage structure of size 2.0 m x 1.5 m x 1.5 m was designed and constructed for fluoride affected villages.
- A cover in two splits was also designed to cover the tank to minimize evaporation losses and also to check contamination risk of stored water. The side space between brick wall and soil was filled in layers for several days for minimizing the air entrapment and provide strength to the side wall.
- The expenditure involved in the construction of rain water storage structure was Rs. 12000.00.
- Seepage and evaporation losses were minimum when covered with a plastic sheets from all around.


D.Crop Improvement for Salinity, Alkalinity and Waterlogged Stresses
Varieties developed and recommended for Salt-affected Soils in U.P.
Rice
Variety : CSR43

- Year of release : 2011
- Duration : 110 days
- Salinity tolerance : 7.0 dS m-1
- Sodicity tolerance : 9.5 pH2
- Yield under stress : 35 q ha-1
- Yield under normal : 65 q ha-1
Variety : CSR46

- Year of release : 2016
- Duration : 130 days
- Salinity tolerance : 9.0 dS m-1
- Sodicity tolerance : 9.9 pH2
- Yield under stress : 40 q ha-1
- Yield under normal : 70 q ha-1
Variety : CSR76
- Year of release : 2021

- Duration : 125-130 days
- Salinity tolerance : 9.0 dS m-1
- Sodicity tolerance : 9.98 pH2
- Yield under stress : 35-40 q ha-1
- Yield under normal : 65-70 q ha-1
Wheat

Variety : KRL283
- Year of release : 2016
- Duration : 139 days
- Salinity tolerance : 6.7 dS m-1
- Sodicity tolerance : 9.3 pH2
- Yield under stress : 45-48 q ha-1
- Yield under normal : 57 q ha-1
Mustard

Variety : CS61
- Year of release : 2023
- Duration : 130-136 days
- Salinity tolerance : 11 dS m-1
- Sodicity tolerance : 9.3 pH2
- Yield under stress : 21-22 q ha-1
- Yield under normal : 25-28 q ha-1
Variety : CS62

- Year of release : 2023
- Duration : 125-132 days
- Salinity tolerance : 12 dS m-1
- Sodicity tolerance : 9.4 pH2
- Yield under stress : 20-22 q ha-1
- Yield under normal : 25-27 q ha-1
New Initiatives
Introduction of Pearl Millet
To test the feasibility of millets as Kharif crop alternative to rice, experiments were initiated where a set of pearl millet hybrids are currently being assessed for performance under high sodicity at vegetative and reproductive stage. Additionally, a set of ~700 pearl millet germplasm from native and global collections were procured from ICRICAT and ICAR-NBPGR which are currently being multiplied.


E. Horticulture and Agroforestry
Identification of sodicity tolerant Jatropha genotypes
- Identified highly salt tolerant Jatropha genotype for producing high biomass and bioenergy besides offering a sustainable amelioration of salt affected soils.
- Jatropha genotype BTP 1-A was found highly suitable for rehabilitation of sodic lands.
- It is recommended that this genotype can perform well in sodic soils having ESP up to 40.
- It can produce a reasonably good oil yield within a short period of time with minimum inputs.
Alternate land uses for bio-amelioration of sodic soils
- Restoration of alkaline soil under tree plantation has improved provisional and supporting ecosystem services and promising species are identified as Prosopis juliflora, Acacia nilotica and Casurina equisetifolia for this purpose.
- P.juliflora is a high biomass producer also alleviates sodicity stress to considerable extent. C. equisetifolia also found promising for improving soil physical and biological properties.
- The degraded sodic lands which are lying unused can be restored for productive purposes by planting P. juliflora, C. equisetifolia and A. nilotica successfully.
Multiple auger planting technique for perennial fruit crops
- A multiple auger hole system got designed, developed and fabricated in collaboration of ICAR- Indian Institute of Sugarcane Research, Lucknow.
- A multiple auger hole was made in partially reclaimed sodic soil. Central auger has 0.30 m diameter and outer auger has 0.15 m diameter. Five auger hole system was adapted in the field for its evaluation in partially reclaimed sodic soil of Shivri Research Farm.
- Apple Ber was planted in the hole. Crop performance so far is outstanding and fruiting initiated within six months of planting.
- Technique would be good for banana, papaya and other crops too. This is an innovative plantation technique.



Salt tolerant mango rootstocks


- Under field studies in typical sodic soils of pH 9.4 the accessions ML-2 and ML-6 showed complete tolerance compared to the check 13-1 while others failed to establish due to continuous exposure to natural salinity.
- The mechanism involved in salt tolerance was studied in detail and was attributed to the sodium exclusion phenomenon occurring at stem region and also effective phenolics release attribute of the rootstock.
- The ML-2 of mango got registered by Plant Germplasm Registration Committee (PGRC) of ICAR on July 2022 vide registration No. INGR22094
New initiatives
- Introduction of Date Palm


Four varieties along with one male of date palm has been introduced from Advance Centre for Date Palm, Bhojka Government of Rajasthan. Two set of experiments one each in pH 8.5 and 10.5 were framed. In both experiments, all varieties were established well under both soil pH.
Facilities
-
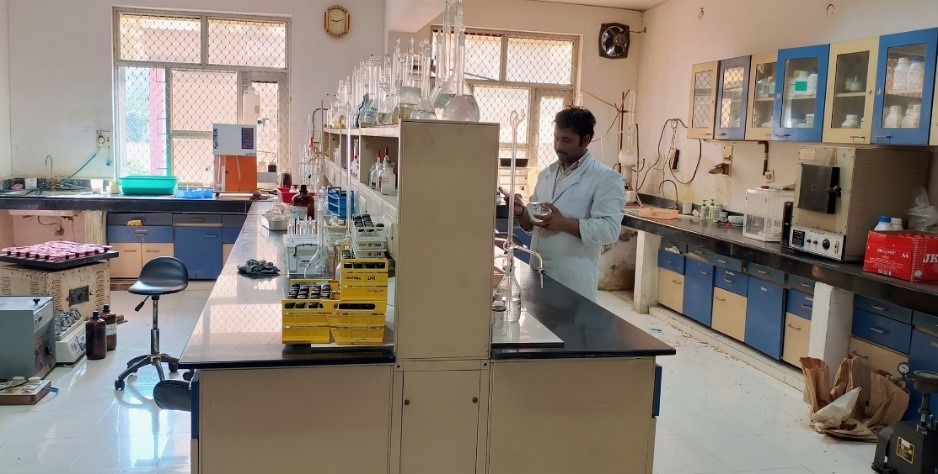
Laboratories
Well equipped state of the art laboratory facilities at RRS, Lucknow
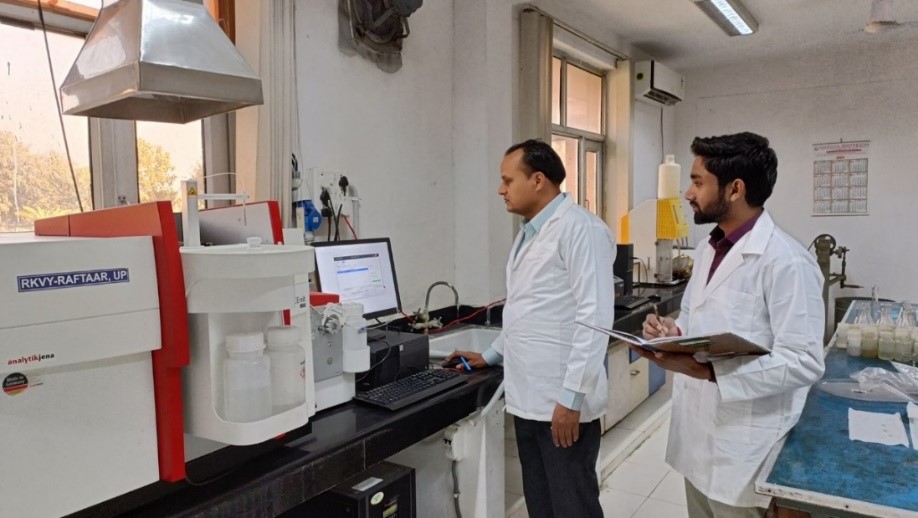
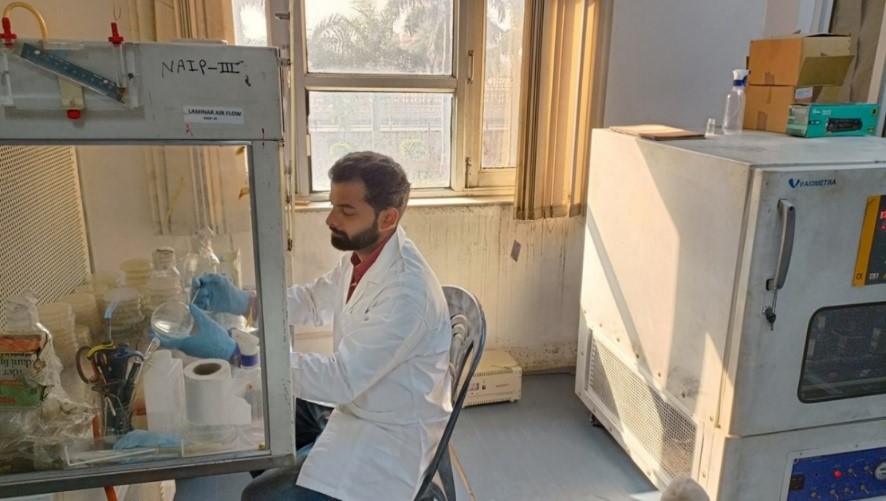




Microbial bio-formulation mass multiplication facility
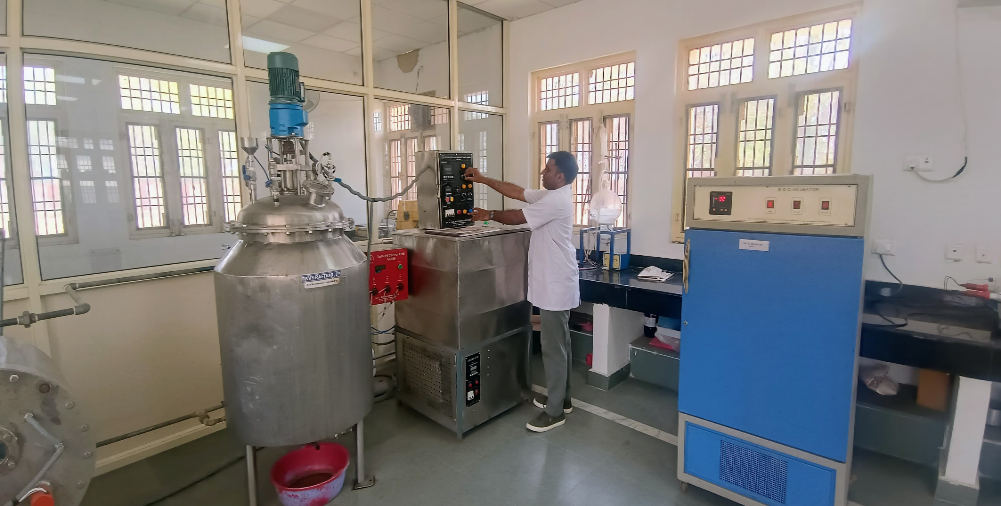
The facility has been developed under the RKVY-RAFTAAR, UP project for mass production of commercialized microbial bioformulation developed at RRS Lucknow. The facility is divided into three sections for (1) microbial quality control for establishing physical and genetic purity of microbial agents, (2) biofermentation lab for rapid mass production of the bioformulation and (3) packaging unit. Facility houses trinocular microscope, thermal cycler, Gel imager, horizontal laminar air flow and a 100 liter capacity batch fermentor.

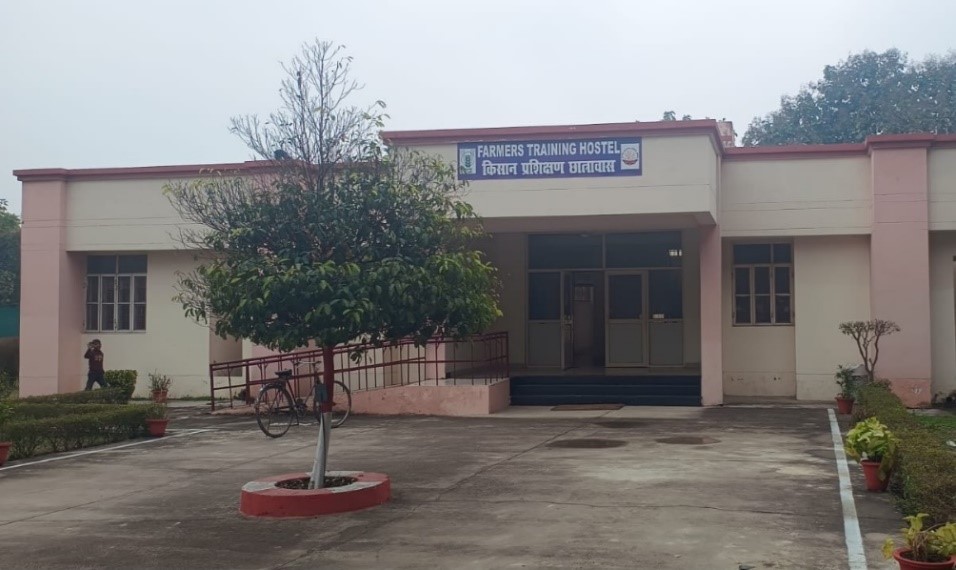
2. Training Hostel
One training hostel for farmers having five AC rooms with double beds.

3.Smart Classroom

4. Conference Hall

5.Experimental Farm
Shivri Farm of CSSRI-RRS, Lucknow
- The Research farm of the ICAR-CSSRI, RRS, Lucknow, spread in 24 hectares of sodic land is situated in village Shivri, Post Kakori, Tehsil Sarojninagar, District Lucknow.
- The research farm possesses unique facilities for experimentation on crop improvement, sodicity management, natural resource management, etc. and demonstration of models of crop production, horticulture, agroforestry, integrated farming system (IFS), organic farming, natural farming, etc. To cater the need of field experimentation, research farm is equipped with agro-met observatory, farm machinery (two tractors, lazer leveler, seed drill, happy seeder, cultivator, harrow, soil turning plough, trolley, bund maker, two power tillers, multi whole making augur, etc.), irrigation facility (Tube wells and solar pump), farm office, store, etc.
- Along with field research, research farm is also involved in seed production of important sodicity tolerant varieties of rice, wheat and mustard.
- It provides an environment to researchers to conduct their field research activities and demonstrate the developed technology for sodic ecosystem.




Farm Implements




Contact Details
- Head : Dr. Anil Kumar Dubey
- E-mail : headcssrirrsl@icar.gov.in
- Mobile : 9868934580
- Address : old Jail Road, Near Manyawar Kanshiram Smarak Sthal, Alambagh Pin 226002, Lucknow UP